Today Google updated the stable version of its Chrome browser to version 36.0.1985.122 on Windows, OS X, and Linux. The update contains a couple of visual changes as well as some under the hood. Chrome OS on the Samsung and Acer ChromeBooks is 32bit. January 23, 2016 at 8:19:36 AM UTC+10, JR Namida wrote: On Thursday, November 24, 2011 at 1:43:29 AM.
This component, known as crosvm, runs untrusted operating systems along with virtualized devices. No actual hardware is emulated. This only runs VMs through the Linux's KVM interface. What makes crosvm unique is a focus on safety within the programming language and a sandbox around the virtual devices to protect the kernel from attack in case of an exploit in the devices.
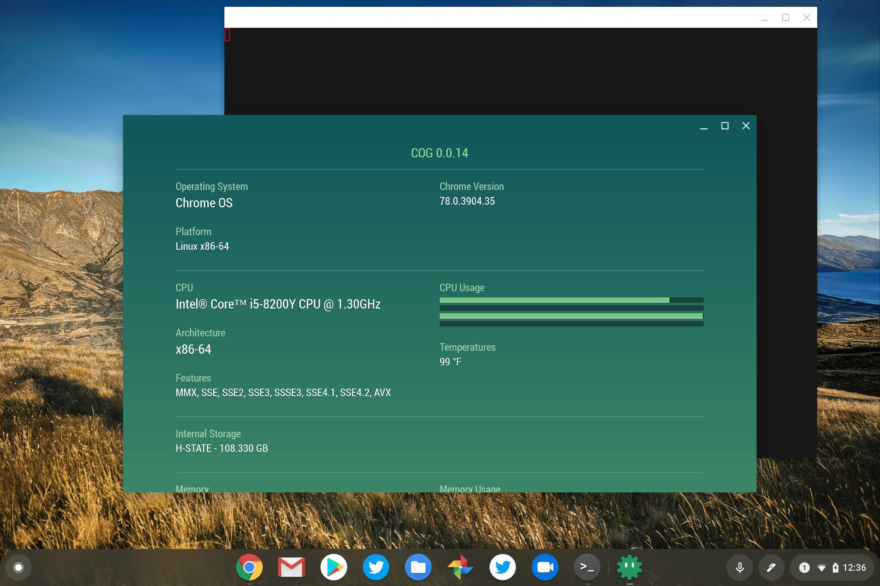
Usage
Google Chrome 36
To see the usage information for your version of crosvm, run crosvm or crosvm run --help.
Boot a Kernel
To run a very basic VM with just a kernel and default devices:
The uncompressed kernel image, also known as vmlinux, can be found in your kernel build directory in the case of x86 at arch/x86/boot/compressed/vmlinux.
Rootfs
In most cases, you will want to give the VM a virtual block device to use as a root file system:
The root image must be a path to a disk image formatted in a way that the kernel can read. Typically this is a squashfs image made with mksquashfs or an ext4 image made with mkfs.ext4. By using the -r argument, the kernel is automatically told to use that image as the root, and therefore can only be given once. More disks can be given with -d or --rwdisk if a writable disk is desired.
To run crosvm with a writable rootfs:
WARNING: Writable disks are at risk of corruption by a malicious or malfunctioning guest OS.
NOTE: If more disks arguments are added prior to the desired rootfs image, the root=/dev/vda must be adjusted to the appropriate letter.
Control Socket
If the control socket was enabled with -s, the main process can be controlled while crosvm is running. To tell crosvm to stop and exit, for example:
NOTE: If the socket path given is for a directory, a socket name underneath that path will be generated based on crosvm's PID.
WARNING: The guest OS will not be notified or gracefully shutdown.
This will cause the original crosvm process to exit in an orderly fashion, allowing it to clean up any OS resources that might have stuck around if crosvm were terminated early.
Chrome Version 36
Multiprocess Mode
To run crosvm in multiprocess mode, use the -u flag. Each device that supports running inside of a sandbox will run in a jailed child process of crosvm. The appropriate minijail seccomp policy files for the running architecture must be in the current working directory.
Virtio Wayland
Virtio Wayland support requires special support on the part of the guest and as such is unlikely to work out of the box unless you are using a Chrome OS kernel along with a termina rootfs.
To use it, ensure that the XDG_RUNTIME_DIR enviroment variable is set and that the path $XDG_RUNTIME_DIR/wayland-0 points to the socket of the Wayland compositor you would like the guest to use.
Defaults
The following are crosvm's default arguments and how to override them.
- 256MB of memory (set with
-m) - 1 virtual CPU (set with
-c) - no block devices (set with
-r,-d, or--rwdisk) - no network (set with
--host_ip,--netmask, and--mac) - virtio wayland support if
XDG_RUNTIME_DIRenviroment variable is set (disable with--no-wl) - only the kernel arguments necessary to run with the supported devices (add more with
-p) - run in single process mode (run in multiprocess mode with
-u) - no control socket (set with
-s)
System Requirements
A Linux kernel with KVM support (check for /dev/kvm) is required to run crosvm. In order to run certain devices, there are additional system requirements:
virtio-wayland- Thememfd_createsyscall, introduced in Linux 3.17, and a Wayland compositor.vsock- Host Linux kernel with vhost-vsock support, introduced in Linux 4.8.multiprocess- Host Linux kernel with seccomp-bpf and Linux namespaceing support.virtio-net- Host Linux kernel with TUN/TAP support (check for/dev/net/tun) and running withCAP_NET_ADMINprivileges.
Emulated Devices
| Device | Description |
|---|---|
CMOS/RTC | Used to get the current calendar time. |
i8042 | Used by the guest kernel to exit crosvm. |
serial | x86 I/O port driven serial devices that print to stdout and take input from stdin. |
virtio-block | Basic read/write block device. |
virtio-net | Device to interface the host and guest networks. |
virtio-rng | Entropy source used to seed guest OS's entropy pool. |
virtio-vsock | Enabled VSOCKs for the guests. |
virtio-wayland | Allowed guest to use host Wayland socket. |
Contributing
Code Health
build_test
There are no automated tests run before code is committed to crosvm. In order to maintain sanity, please execute build_test before submitting code for review. All tests should be passing or ignored and there should be no compiler warnings or errors. All supported architectures are built, but only tests for x86_64 are run. In order to build everything without failures, sysroots must be supplied for each architecture. See build_test -h for more information.
rustfmt
New code should be run with rustfmt Os x yosemite is free. , but not all currently checked in code has already been autoformatted. If running rustfmt causes a lot of churn for a file, do not check in lines unrelated to your change.
Dependencies
With a few exceptions, external dependencies inside of the Cargo.toml files are not allowed. The reason being that community made crates tend to explode the binary size by including dozens of transitive dependencies. All these dependencies also must be reviewed to ensure their suitability to the crosvm project. Currently allowed crates are:
Office 365 Chrome Os
byteorder- A very small library used for endian swaps.gcc- Build time dependency needed to build C source code used in crosvm.libc- Required to use the standard library, this crate is a simple wrapper aroundlibc's symbols.
Code Overview
The crosvm source code is written in Rust and C. To build, crosvm requires rustc v1.20 or later.
Source code is organized into crates, each with their own unit tests. These crates are:
crosvm- The top-level binary front-end for using crosvm, along with all devices.io_jail- Creates jailed process usinglibminijail.kernel_loader- Loads elf64 kernel files to a slice of memory.kvm_sys- Low-level (mostly) auto-generated structures and constants for using KVM.kvm- Unsafe, low-level wrapper code for usingkvm_sys.net_sys- Low-level (mostly) auto-generated structures and constants for creating TUN/TAP devices.net_util- Wrapper for creating TUN/TAP devices.sys_util- Mostly safe wrappers for small system facilities such aseventfdorsyslog.syscall_defines- Lists of syscall numbers in each architecture used to make syscalls not supported inlibc.vhost- Wrappers for creating vhost based devices.virtio_sys- Low-level (mostly) auto-generated structures and constants for interfacing with kernel vhost support.x86_64- Support code specific to 64 bit intel machines.
The seccomp folder contains minijail seccomp policy files for each sandboxed device. Because some syscalls vary by architecturs, the seccomp policies are split by architecture.
Google has issued a new stable release of Chrome OS. Version 35, which hit beta last month, is rolling out to all Chromebook owners as of today.
Chrome OS 35 Stable features a number of key improvements aimed at enhancing the user experience of Chromebooks, ‘boxes and ‘bases all over the world.
But which new features are the most notable? Let's take a look.
App List Folders
Google browser for windows 7. Folder creation in the app launcher finally arrives to all, having spent several months being tested in dev and beta channels.
With folders you can group installed apps however you like — from a ‘Google folder' for Docs, YouTube and Keep, to a ‘games' directory housing Angry Birds,2048, and similar.
To create a new folder:
- Open the Apps List
- Long press on an app icon to ‘pick it up'
- Drag it over another icon until a dark circle appears
- Let it go to create a folder containing both items
You can drag and drop more apps onto the folder icon to add them. Having created a folder you may next want to give it a name:
- Click on the folder you want to rename to open it
- Click the heading ‘untitled folder'
- Enter a new name
- Hit Enter/Return
To delete a folder you will need to drag out each item within it. Google android vm. When only one item is left the folder will automatically delete itself*.
Improved Window Controls
Chrome Os 365
You may not have noticed, but a few releases back Google removed the ‘minimise' window control. The theory was, since you can minimise by clicking on the app shelf icon an entry in the window frame was largely redundant. Well, seemingly not; based on user feedback the minimise button has returned.
Also new to this release is an improved way to ‘snap' windows to the left and right ends of the screen. Long-press on the maximise button and drag towards the direction you would like the app window to resize to.
Ok Google!
If you're in the US (or using US English as your default language) you can play with ‘Ok Google' hotword detection in the app launcher and on the Google.com new tab page.
When either of these is open simply say ‘Ok Google' to trigger voice search.
In addition to providing web results from Google.com you can launch installed applications by speaking their name. Neat, right?
Captive Portal Detection
If you're a frequent user of public Wi-Fi you'll be familiar with ‘captive portals' — additional steps to sign into Wi-Fi in cafes, hotels and so on. This update implements captive portal detection for a signed-in session, nixing the hoops you previously needed to jump through to get online.
Other Changes
In addition to a smattering of changes you can see are a legion more you can't. Chrome OS 35 features a barrage of bug fixes and security updates.
Google Chrome OS 35 is rolling out to stable channel users on all devices except for the ASUS and Samsung Chromeboxes. Chrome automatically downloads and installs updates in the background, but you can force a check by going to ‘chrome://chrome' in a new tab.
If you don't see an update waiting don't panic — these things take place in stages over a 24-48 hour period.
*The ‘Samsung' and ‘Asus' folders cannot be deleted this way on select models
